About UNODC
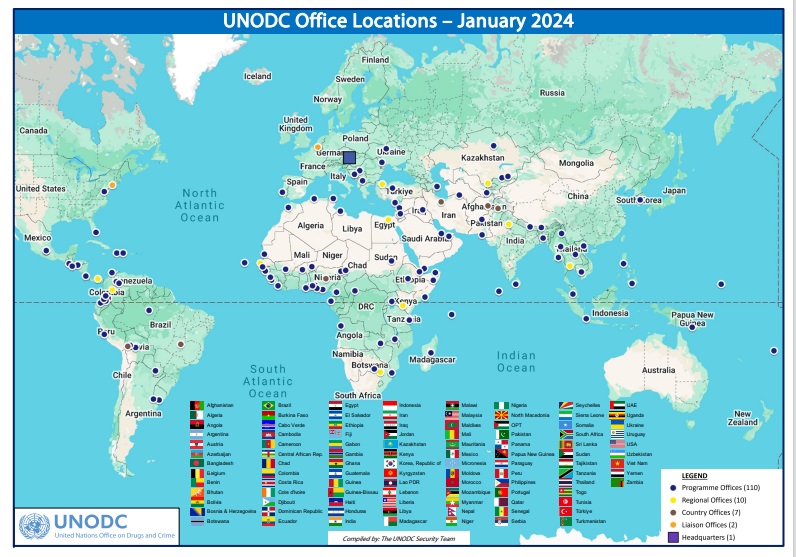
UNODC is based in Vienna, Austria, and is present in all regions of the world through its global programmes. The Office emplyes 2,500 people and works in a network of field offices in 80 countries
UNODC has been in Brazil since 1991, where it has a Liaison and Partership Office in Brasília (DF) and employs people in almost the 27 Brazilian Federation Units.
Always supported by scientific evidence, UNODC works directly with governments, ministries, security forces, justice, health and penitentiary systems at the federal, state and municipal levels and has a technical and operational team of about 90 professionals in Brazil, specialized in the programmatic areas of the Office.
About the Liaison and Partnership Office in Brazil
UNODC bases its work on the three international drug control conventions, the conventions against transnational organised crime and against corruption and the international instruments against terrorism.
UNODC's goal is to make the world safer from drugs, organised crime, corruption and terrorism by combating these threats to achieve health, security and justice for all and by promoting sustainable peace and well-being.
UNODC provides technical assistance to Member States in the areas of health, criminal justice and public security, including drug use control and prevention, tackling transnational organized crime, illicit trafficking in drugs, human beings and arms, prison reform, corruption and money laundering, asset management and recovery, and HIV prevention among drug users and people in detention.
United Nations Conventions
UNODC, as the guardian of the following conventions ratified by Brazil, has the mandate to support countries in their implementation:
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (Palermo Convention/UNTOC) and its protocols on trafficking in persons; smuggling of migrants; and illicit trafficking in firearms
- UN Convention against Corruption (UNCAC)
- UN Conventions on Drugs (1961, 1971, 1988)
- UN Conventions on Terrorism (1963, 1970, 1971, 1973, 1979, 1980, 1988, 1991, 1997, 1999, 2005, 2010, 2014)
- United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners (Mandela Rules)
Pillars of our work
Normative work, to assist in the ratification and implementation of international treaties, and the development of national legislation on drugs, crime and terrorism.
Research and analysis, to enrich knowledge and broaden understanding of drug and crime problems and to establish evidence-based policies and strategies.
Technical assistance through international cooperation, to enable Member States to provide effective responses to drug-related issues, organized crime and terrorism.
UNODC works in partnership with the Brazilian government in different areas:
UNODC and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)
UNODC is committed to supporting Member States in the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development which recognizes that the rule of law, effective and humane security and justice systems, health promotion and drug use prevention, are part of sustainable development.
Our projects in Brazil
 |
Center for Drug Study and Community Social Development (Cdesc)
Produce evidence-based studies and analyses, taking a multidimensional approach to the issue of drugs, seeking to foster social, economic and environmental alternatives that promote the sustainable development of communities affected by drug trafficking in urban and rural areas.
|
 |
Support for the Implementation of the National System for the Prevention of the Use of Alcohol and Other Drugs (Sinap)
Support the federal government in the institutionalization of the National System for the Prevention of the Use of Alcohol and Other Drugs (Sinap) through an information platform for the public and through the access to information and tools to prevent the use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs.
|
 |
Organized Crime in Prisons and Drug Trafficking in a Regional Perspective (PRIS-COOP)
Promote the use of innovative and interagency practices to improve the management of the prison system, focusing on the challenges generated by organized crime in prisons and encourage cooperation with Paraguay, Peru, and Colombia.
|
 |
Trafficking in Persons and Smuggling of Migrants (Track for Tip - T4T)
Improve the criminal justice response to human trafficking in the migratory flows of eight countries in South America and the Caribbean (Aruba, Brazil, Colombia, Curaçao, Ecuador, Peru, Dominican Republic and Trinidad and Tobago), as well as improving statistical data in people’s usual traffic area, especiallyVenezuelans.
|
 |
Container Control Programme (CCP)
Provide expert assistance to minimize the illicit trafficking of drugs and other illicit goods in maritime containers in more than 70 Member States.
|
 |
CRIMJUST
Fight drug trafficking and organized crime along certain routes in Latin America, Africa and Europe, promoting regional cooperation in Dominican Republic, Panama, Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico, Peru, Paraguay, Uruguay, Honduras, Guatemala, Costa Rica and El Salvador.
|
 |
AIRCOP
Strengthen cooperation between international airports in over 30 Member States to detect and intercept drugs and other illicit goods
|
 |
TAPAJÓS - Prevalence Project to Reduce Forced Labour in the Gold Mining Sector in the State of Pará
Promote evidence-based studies on the prevalence of human trafficking and slave labour and on interstate mobility and socioethnographic profile of victims (Maranhão - Pará).
|
 |
Law Enforcement Assistance Programme to Reduce Tropical Deforestation (LEAP)
Share knowledge and build global networks to combat the illicit timber trade and crime in South Asia and
Latin America (Peru, Ecuador, Brazil, Colombia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Cambodia).
|
 |
Regional Cooperation to Address Environmental Crimes (ECOS)
Provide technical assistance to criminal justice systems in the detection, interception, investigation, and repression of crimes that affect the environment in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru and Suriname.
|
 |
Strengthening the Criminal Justice System Response to Forestry Crimes (CRIMFLO)
Improve national interagency and crossborder coordination and promote best practices for judges and prosecutors at the state and federal levels through specialized manuals and courses.
|
 |
Global Maritime Crime Programme (GMCP)
Strengthen Brazil’s interagency capacity and cross-border cooperation in drug trafficking on rivers and ports, in cooperation with neighbouring countries.
|
 |
Violence and Drug Prevention in Pernambuco
Create a matrix of indicators to monitor different policies for crime, violence and drugs prevention, and research treatment services aimed at people with problems associated with the harmful use of alcohol and/or other drugs.
|
 |
Youth Ambassadors
Reduce youth crime throughcitizen participation and contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
|
 |
Global Action for Business Integrity
Develop innovative and sustainable solutions to prevent and combat corruption, favouring public-private dialogue in accordance with the UNCAC in seven countries (Saudi Arabia, Brazil, Colombia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Malaysia, Uzbekistan).
|
Our main donors